Page 50 - Zmist-n2-2015
P. 50
Experimental studies. Preparation of experimental materials. In this study, the
pure PTFE, C-PTFE, B-PTFE and G-PTFE particle reinforced materials have been
used as journal bearing and SAE 1050 material as a shaft. The chemical compositions
of the journal material used in the experiments are (%): 0.51 C; 0.3 Si; 0.7 Mn; 0.04 P;
0.05 S; balance Fe. Dimensions of bearing specimens were as follows: inner diameter
+0.05
(d = 10 mm), width (B = 10 mm), outer diameter (D = 15 mm).
The specimens have been worn and friction coefficients have been measured on
radial journal bearing wear test rig in dry conditions as described by Atik et al. [18] and
Ünlü and Atik [19]. The wear losses have been measured in dry conditions with 20 N
loads, 250 rpm (v = 0.130 m/s) and every 30 min for 2.5 h (1177.5 m sliding distance).
The specimens were cleaned by acetone. The microstructures of the specimens wear
surfaces have been photographed using the optical microscope (Hund Wetzlar
CCD-290) and scanning electron microscope (Jeol JSM-6060).
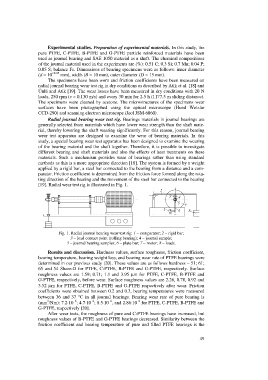
Radial journal bearing wear test rig. Bearings materials in journal bearings are
generally selected from materials which have lower wear strength than the shaft mate-
rial, thereby lowering the shaft wearing significantly. For this reason, journal bearing
wear test apparatus are designed to examine the wear of bearing materials. In this
study, a special bearing wear test apparatus has been designed to examine the wearing
of the bearing material and the shaft together. Therefore, it is possible to investigate
different bearing and shaft materials and also the effects of heat treatments on these
materials. Such a mechanism provides wear of bearings rather than using standard
methods as this is a more appropriate direction [18]. The system is formed by a weight
applied by a rigid bar, a steel bar connected to the bearing from a distance and a com-
parator. Friction coefficient is determined from the friction force formed along the rota-
ting direction of the bearing and the movement of the steel bar connected to the bearing
[19]. Radial wear test rig is illustrated in Fig. 1.
Fig. 1. Radial journal bearing wear test rig: 1 – comparator; 2 – rigid bar;
3 – load contact point (rolling bearing); 4 – journal sample;
5 – journal bearing samples; 6 – plate bar; 7 – motor; 8 – loads.
Results and discussion. Hardness values, surface roughness, friction coefficient,
bearing temperature, bearing weight loss, and bearing wear rate of PTFE bearings were
determined in our previous study [20]. These values are as follows hardness – 51; 61;
65 and 54 Share-D for PTFE, C-PTFE, B-PTFE and G-PTFE, respectively. Surface
roughness values are 1.59; 0.71; 1.1 and 3.95 mm for PTFE, C-PTFE, B-PTFE and
G-PTFE, respectively, before wear. Surface roughness values are 2.26, 0.78, 0.92 and
3.52 mm for PTFE, C-PTFE, B-PTFE and G-PTFE respectively after wear. Friction
coefficients were obtained between 0.2 and 0.3, bearing temperatures were measured
between 36 and 37 °C in all journal bearings. Bearing wear rate of pure bearing is
3 –6 –6 –6 –6
(mm /Nm): 7.2×10 ; 4.7×10 ; 8.5×10 , and 2.86×10 for PTFE, C-PTFE, B-PTFE and
G-PTFE, respectively [20].
After wear tests, the roughness of pure and C-PTFE bearings have increased, but
roughness values of B-PTFE and G-PTFE bearings decreased. Similarity between the
friction coefficient and bearing temperature of pure and filled PTFE bearings is the
49