Page 51 - Zmist-n2-2015
P. 51
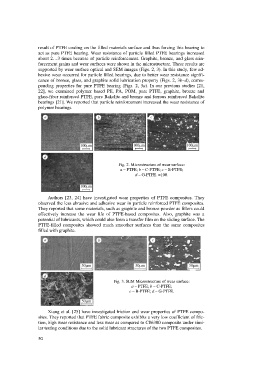
result of PTFE coating on the filled materials surface and thus forcing this bearing to
act as pure PTFE bearing. Wear resistance of particle filled PTFE bearings increased
about 2…3 times because of particle reinforcement. Graphite, bronze, and glass rein-
forcement grains and wear surfaces were shown in the microstructure. These results are
supported by wear surface optical and SEM images (Figs. 2, 3). In this study, few ad-
hesive wear occurred for particle filled bearings, due to better wear resistance signifi-
cance of bronze, glass, and graphite solid lubrication property (Figs. 2, 3b–d), corres-
ponding properties for pure PTFE bearing (Figs. 2, 3a). In our previous studies [21,
22], we examined polymer based PE, PA, POM, pure PTFE, graphite, bronze and
glass-fiber reinforced PTFE, pure Bakelite and bronze and ferrous reinforced Bakelite
bearings [21]. We reported that particle reinforcement increased the wear resistance of
polymer bearings.
Fig. 2. Microstructure of wear surface:
a – PTFE; b – C-PTFE; c – B-PTFE;
d – G-PTFE. ´100.
Authors [23, 24] have investigated wear properties of PTFE composites. They
observed the less abrasive and adhesive wear in particle reinforced PTFE composites.
They reported that some materials, such as graphite and bronze powder as fillers could
effectively increase the wear life of PTFE-based composites. Also, graphite was a
potential of lubricants, which could also form a transfer film on the sliding surface. The
PTFE-filled composites showed much smoother surfaces than the same composites
filled with graphite.
Fig. 3. SEM Microstructure of wear surface:
a – PTFE; b – C-PTFE;
c – B-PTFE; d – G-PTFE.
Xiang et al. [25] have investigated friction and wear properties of PTFE compo-
sites. They reported that PTFE fabric composite exhibits a very low coefficient of fric-
tion, high wear resistance and less wear as compared to C86300 composite under simi-
lar testing conditions due to the solid lubricant structures of the two PTFE composites.
50