Page 72 - Zmist-n3-2015-new
P. 72
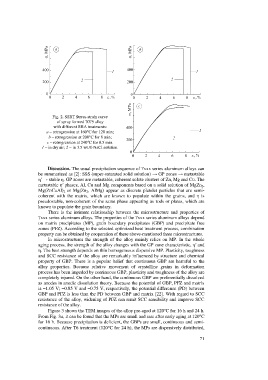
Fig. 2. SSRT Stress-strain curve
of spray formed 7075 alloy
with different RRA treatments:
a – retrogression at 160°C for 120 min;
b – retrogression at 200°C for 8 min;
c – retrogression at 240°C for 0.5 min.
1 – in dry air; 2 – in 3.5 wt.% NaCl solution.
Discussion. The usual precipitation sequence of 7xxx series aluminum alloys can
be summarized as [2]: SSS (super-saturated solid solution) → GP zones → metastable
η′ → stable η. GP zones are metastable, coherent solute clusters of Zn, Mg and Cu. The
metastable η′ phases, Al, Cu and Mg components based on a solid solution of MgZn 2,
Mg(ZnCuAl) 2 or Mg(Zn 2, AlMg) appear as discrete platelet particles that are semi-
coherent with the matrix, which are known to populate within the grains, and η is
pseudostable, non-coherent of the same phase appearing as rods or plates, which are
known to populate the grain boundary.
There is the intimate relationship between the microstructure and properties of
7xxx series aluminum alloys. The properties of the 7xxx series aluminum alloys depend
on matrix precipitates (MP), grain boundary precipitates (GBP) and precipitate free
zones (PFZ). According to the selected optimized heat treatment process, combination
property can be obtained by cooperation of these above-mentioned three microstructures.
In microstructures the strength of the alloy mainly relies on MP. In the whole
aging process, the strength of the alloy changes with the GP zone characteristic, η′ and
η. The best strength depends on thin homogeneous dispersive MP. Plasticity, toughness
and SCC resistance of the alloy are remarkably influenced by structure and chemical
property of GBP. There is a popular belief that continuous GBP are harmful to the
alloy properties. Because relative movement of crystalline grains in deformation
process has been impeded by continuous GBP, plasticity and toughness of the alloy are
completely injured. On the other hand, the continuous GBP are preferentially dissolved
as anodes in anodic dissolution theory. Because the potential of GBP, PFZ and matrix
is −1.05 V; −0.85 V and −0.75 V, respectively, the potential difference (PD) between
GBP and PFZ is less than the PD between GBP and matrix [22]. With regard to SCC
resistance of the alloy, widening of PFZ can remit SCC sensibility and improve SCC
resistance of the alloy.
Figure 3 shows the TEM images of the alloy pre-aged at 120°C for 16 h and 24 h.
From Fig. 3a, it can be found that the MPs are small and rare after early aging at 120°C
for 16 h. Because precipitation is deficient, the GBPs are small, continuous and semi-
continuous. After T6 treatment (120°C for 24 h), the MPs are dispersively distributed,
71