Page 139 - Zmist-n4-2015
P. 139
where e is the strain value; a is the lattice parameter; D is the grain size.
The stress was calculated by using the formulae:
E a - a
S = 0 (5)
2d a 0
The FWHM is calculated by the equation,
b = (2 high 2 low)Xq - q ( /180p ) (6)
The lattice parameter was determined for each of the diffracting planes from XRD
patterns.
2
2
1 h + k + l 2
2 = 2 ,
d a
where E is the Young’s modulus of the powder; δ is the Poission’s ratio of the pow-
ders; a 0 is the bulk lattice constant and a is lattice constant of the powders. In order to
study the compressibility of the different powder blends, the density after compaction
at pre-determined pressure was measured and recorded. The compressibility of powder
mixtures were carried out using computerized universal testing machine of 400 kN
capacity (Venus Instruments, India; Model: UTV-40PC, SR No.: 2011/[4084]) with
suitable punch and die. The known values of relative densities and applied pressure
have been used in the Heckel and Balshin compaction equation to validate the results.
Standard deviation from the linearity of the measured values and regression equations
for all samples were determined using Origin-8 software.
The milled Al + 5% TiO 2 + 6% Gr hybrid composite powders were compacted in
400 kN hydraulic press using punch and die. The compaction pressure was 500 MPa
and the specimen dimensions were 24 mm diameter and 12 mm height. The sintering
was done in a muffle furnace at the temperature of 590°C for a period of 3 h. The SEM
analysis of the sintered Al + 5% TiO 2 + 6% Gr composite was conducted using FEI
Quanta FEG 200-SEM. The microstructure analyses were carried out for the sintered
hybrid composite specimen using an optical microscope and image analyzing software
(Media Image Technologies Pvt. Ltd. Hyderabad) to study the grain boundary, bonding
between the matrix and reinforcements.
Results and discussion. XRD analy-
sis of milled powders. The XRD patterns
of Al + 0% TiO 2, Al + 5% TiO 2, Al + 5%
TiO 2 + 2% Gr and Al + 5% TiO 2 + 4% Gr
composite powders, reported in previous
publication are used to calculate the struc-
tural parameters [12]. In this study XRD
pattern of Al + 5% TiO 2 + 6% Gr compo-
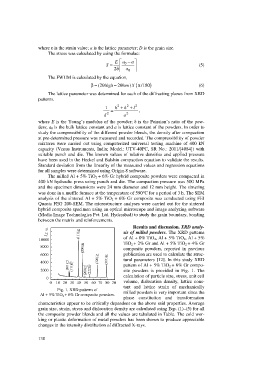
site powders is provided in Fig. 1. The
calculation of particle size, stress, unit cell
volume, dislocation density, lattice cons-
tant and lattice strain of mechanically
Fig. 1. XRD patterns of
Al + 5% TiO 2 + 6% Gr composite powders. milled powders is very important since the
phase constitution and transformation
characteristics appear to be critically dependent on the above said properties. Average
grain size, strain, stress and dislocation density are calculated using Eqs. (1)–(5) for all
the composite powder blends and all the values are tabulated in Table. The cold wor-
king or plastic deformation of metal powders has been shown to produce appreciable
changes in the intensity distribution of diffracted X-rays.
138